The avocado is a tree native to Mexico and Central America, classified in the flowering plant family Lauraceae along with cinnamon, camphor and bay laurel. Avocado or alligator pear also refers to the fruit, botanically a large berry that contains a single seed.
Avocados are commercially valuable and are cultivated in tropical and Mediterranean climates throughout the world. They have a green-skinned, fleshy body that may be pear-shaped, egg-shaped, or spherical. If you smash them and mixed them with chopped tomatoes, onions and garlic, they become the epic green dip known as Guacamole.
Like the avocado, Amadeo Avogadro was born and raised in the Mediterranean climate of Italy (I am really sorry for the pun. It was intended and I couldn’t help it). He was an Italian scientist who was born at Turin to a noble family of Piedmont-Sardinia in the year 1776.  Since childhood, Avogadro had a deep interest in science. Growing up, he was inspired by the works of Galileo and Newton and was sent to school by his father to become a lawyer. He became one and then he did what he really loved. He became the science guy who is most noted for his contributions to molecular theory, including what is known as Avogadro’s law.
Since childhood, Avogadro had a deep interest in science. Growing up, he was inspired by the works of Galileo and Newton and was sent to school by his father to become a lawyer. He became one and then he did what he really loved. He became the science guy who is most noted for his contributions to molecular theory, including what is known as Avogadro’s law.
Avogadro’s law is an experimental gas law relating volume of a gas to the amount of substance of gas present. Avogadro’s law states that, “equal volumes (V) of all gases, at the same temperature and pressure, have the same number of molecules”.
For a given mass of an ideal gas, the volume and amount (n, measured in moles) of the gas are directly proportional if the temperature and pressure are constant.
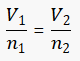
The equation shows that, as the number of moles of gas increases, the volume of the gas also increases in proportion. Similarly, if the number of moles of gas is decreased, then the volume also decreases. Thus, the number of molecules or atoms in a specific volume of ideal gas is independent of their size or the molar mass of the gas.
In tribute to Avogadro, the number of elementary entities (atoms, molecules, ions or other particles) in 1 mole of a substance, 6.02214179(30)×1023 , is known as the Avogadro constant, one of the seven SI base units and represented by NA.
As always, you can try using fxSolver, with Avogadro’s law equation.
Please, remember to follow our social media pages, by hitting the buttons below and watch the fxSolver video as well!
