Well, we all know what an earthquake is, and pretty much how it occurs.
Everyone who has experienced a scary earthquake, wonders if we ever find a way to predict them. Geologists have some theories, but unfortunately, none of them really delivers what is needed. And what is needed is an accurate prediction of earthquakes that will happen soon, not that statistic-based predictions that say “in the next 10-50-100-200 years, a big one will happen in this huge area”.
Here comes the Dilatancy Theory.
When a rock is stressed, it expands. The micro cracks and fractures in the rock are getting larger and larger, after the rock is half way toward its breaking point. The rock changes physically.
This cannot be monitored visually, but it has an impact to the groundwater’s pressure and levels. Scientists figured that out in the past, and monitored all these factors, to find generalized patterns.
With this technique, in the past century Asian scientists managed to predict a catastrophic earthquake event soon enough to save an entire town. Scientists were happy and monitored all these factors with even more detail. They thought they finally had an answer to the problem. Till another huge earthquake, leveled a town without giving any hints before. Nevertheless, these methods are quite successful, in relation to volcanic eruptions.
The Chinese, created a new theory after a 1975 incident. During January, they received reports of strange animal behavior. Large farm animals, had become restless, frightened for no obvious reason and they refused to enter buildings. A month later, a major earthquake struck and the epicenter was in the area with the most abnormal animal behavior reports.
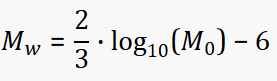
Other formulas regarding Seismology can be found Here.
Please, remember to follow our social media pages, by hitting the buttons below!
